Learning Outcomes in Listing:
i. Define enzyme specificity.
ii. Illustrate the relationship between enzyme shape and specificity with examples.
iii. Understand the implications of enzyme specificity for biological reactions..
Summary of Lesson:
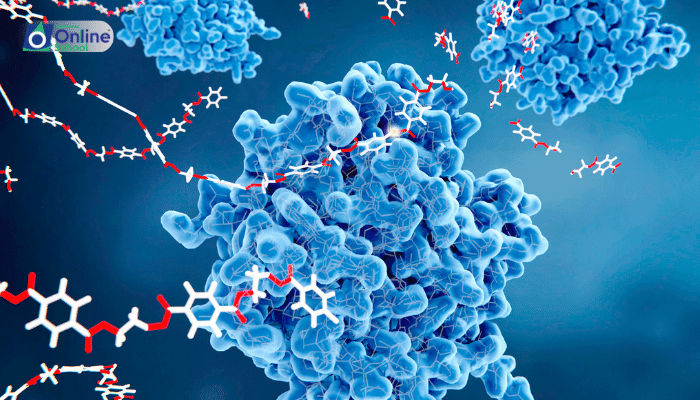
Enzyme specificity is the concept that each enzyme catalyzes only one kind of reaction. This lesson will explain that the specificity of enzymes is largely due to the unique shape of the active site and the specific way in which the substrate fits into it.
Content:
i. Understanding Enzyme Specificity: Enzymes are highly specific, meaning they will only catalyze a reaction for a single type of substrate—a concept often likened to a lock and key mechanism where only the right key (substrate) fits into the lock (enzyme's active site).
ii. Shape Dictates Function:
The shape of an enzyme’s active site is complementary to the shape of its substrate, allowing for precise binding. This specificity is due to the unique arrangement of amino acids that form the active site.
For example, the enzyme sucrase only acts on sucrose because the shape of sucrose fits perfectly into the active site of sucrase. Similarly, lactase will only break down lactose, not other disaccharides.
iii. Implications of Enzyme Specificity:
The specificity of enzymes ensures that reactions occur correctly within the cell, contributing to the efficiency and regulation of the cell's metabolism.
It also means that enzymes can be affected by inhibitors that mimic the substrate's shape, blocking the active site and preventing the enzyme from catalyzing its reaction.
List of Important Questions for Self-Study:
i. Why is enzyme specificity crucial for cellular function?
ii. How does the shape of an enzyme determine its function?
iii. Can an enzyme change its shape to fit different substrates? Why or why not?
iv. What would happen if an enzyme lost its specificity?
v. How do inhibitors take advantage of enzyme specificity?
Important Terminologies Used in Lesson:
Enzyme Specificity: The ability of an enzyme to choose exactly the right substrate from a group of similar molecules.
Active Site: The specific region on an enzyme where the substrate binds.
Substrate: The substance on which an enzyme acts.
Lock and Key Mechanism: A model of enzyme activity that explains how specific enzyme-substrate binding is.
Amino Acids: The building blocks of proteins, which make up the structure of enzymes and determine the shape and function of the active site.